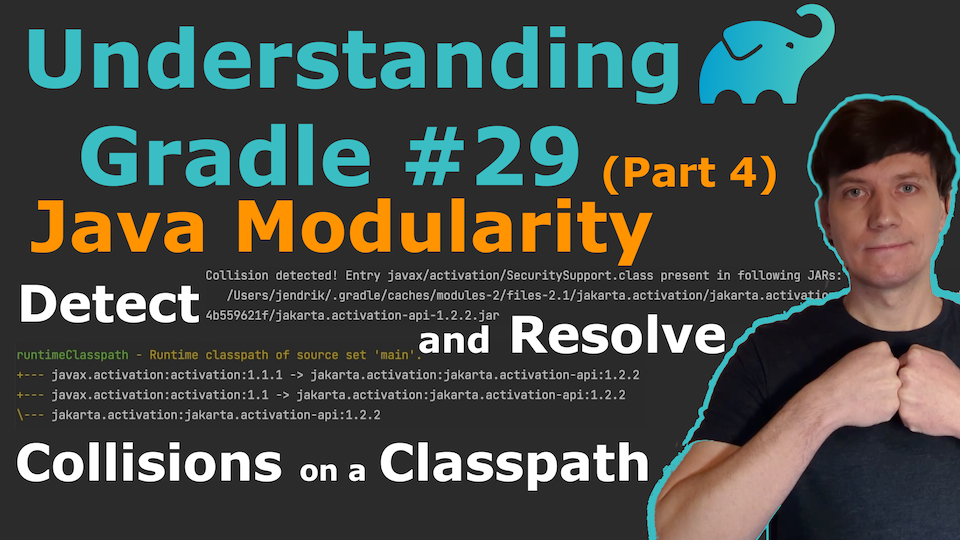
The org.gradlex.jvm-dependency-conflict-detection plugin adds Capabilities
to the metadata of well-known components hosted on Maven Central that are used in many Java projects.
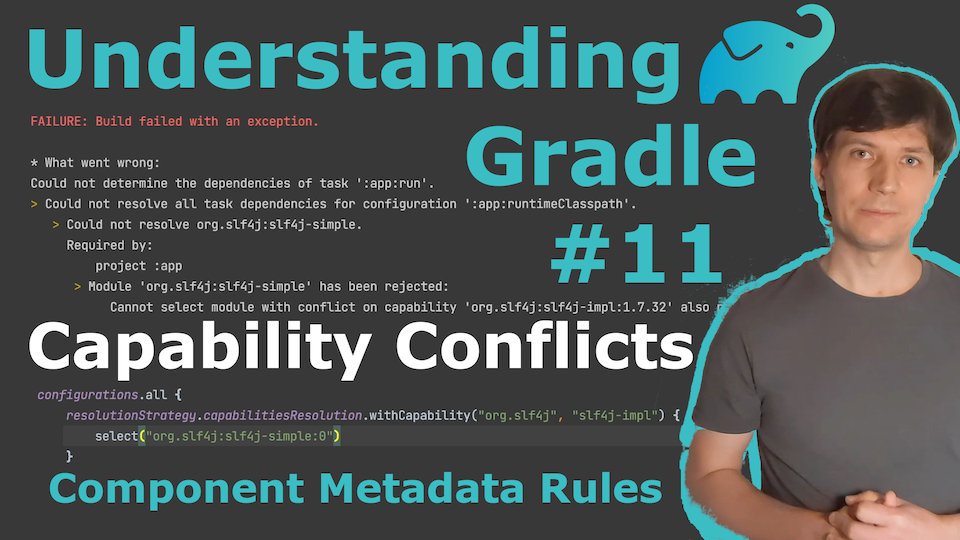
The org.gradlex.jvm-dependency-conflict-resolution plugin offers a compact language to address dependency conflicts by expressing strategies for Gradle to follow or to fix issues in the metadata of published components.
The videos below explain the concept of Capability Conflicts and why they can help you to avoid "dependency hell" in your project. With this plugin, you enable Gradle to detect and automatically resolved typical capability conflicts in the JVM ecosystem.
See the documentation.
- Minimal Gradle version is
6.8.3
Note: There are rules in this plugin (in particular for Guava) which work better with Gradle 7+.
This is because Gradle 7 added support for the org.gradle.jvm.environment attribute that allows Gradle to better distinguish between standard-jvm and android projects.
This plugin collects information for libraries available on Maven Central to allow capability conflict detection. If you discover that information is missing, we appreciate a contribution to the plugin. An indication that such information is missing, is that you have duplicated classes on your classpath although this plugin is active.
You can use the patch DSL to add the missing rule without modifying the plugin. Do this first and verify that it behaves as expected:
// Assuming 'org.example:name' and 'org.example.new:new-name' are in conflict
jvmDependencyConflicts {
patch {
module("org.example:name") { addCapability("org.mydomain:name") }
module("org.example.new:new-name") { addCapability("org.mydomain:name") }
conflictResolution {
selectHighestVersion("com.mydomain:name")
}
}Once you confirmed that the rule is working as expected, you can open a PR in this repository to contribute your findings back to the plugin. This is done as follows:
- Add a new entry to the CapabilityDefinition enum. You can use the ASM entry as orientation.
- Run the
JarOverlapTest. The test will tell you that you need to add dependencies tosamples/sample-all/build.gradle.ktsandsamples/sample-all-deactivated/build.gradle.kts. Lookup the latest versions of the dependencies and add them to the files. This is so that the plugin's test suite can automatically verify that the new entry is valid in the sense that the Jars overlap. Make sueJarOverlapTestpasses after you made the changes. - Run the
SamplesTest. It will tell you thatsamples/sample-all/build.outandsamples/sample-all-deactivated/build.outdo not have the expected content. Update these files accordingly (you may copy the new expected output from the failed test's output). This is the output of Gradle'sdependenciestask. Check that the changes are what you would expect. Make sueSamplesTestpasses after you made the changes.
Create a PR with the changes to the files:
- CapabilityDefinition.java
- samples/sample-all/build.gradle.kts
- samples/sample-all/build.out
- samples/sample-all-deactivated/build.gradle.kts
- samples/sample-all-deactivated/build.out
These plugins join, unify and extend functionalities that were previously part of the following discontinued plugins:
- https://plugins.gradle.org/plugin/org.gradlex.java-ecosystem-capabilities
- https://plugins.gradle.org/plugin/dev.jacomet.logging-capabilities
- https://plugins.gradle.org/plugin/de.jjohannes.java-ecosystem-capabilities
- https://plugins.gradle.org/plugin/de.jjohannes.missing-metadata-guava
If you are migrating from one of these plugins, you can find some information in the following issue. For further questions, please ask in a comment on the issue.
NOTE on Guava:
Some of these plugins are used to patch older versions of Guava.
This functionality is discontinued.
Most of the patching is not included anymore by default, because Guava now publishes richer metadata and some of the adjustments were opinionated.
If you use the latest Guava version, you may not need anything specific.
If some of the transitive dependencies are not wanted in your case, you can fine tune them using the jvmDependencyConflicts.patch DSL. E.g.:
jvmDependencyConflicts {
patch {
module("com.google.guava:guava") {
removeDependency("com.google.code.findbugs:jsr305")
reduceToCompileOnlyApiDependency("com.google.errorprone:error_prone_annotations")
}
}
}If you need the previous behavior for older Guava versions, you can explicitly apply the GuavaComponentRule.
dependencies.components {
withModule<GuavaComponentRule>("com.google.guava:guava")
}Gradle and the Gradle logo are trademarks of Gradle, Inc. The GradleX project is not endorsed by, affiliated with, or associated with Gradle or Gradle, Inc. in any way.